Our website is not supported on this browser
The browser you are using (Internet Explorer) cannot display our content.
Please come back on a more recent browser to have the best experience possible

Project Controls are integral to ensure the quality of a project is to the required standard, and to give direction to the Project Manager with regards to time and cost. The Project Controls Manager (PCM) is responsible for collating and analysing the performance, time and cost data. A PCM plays a crucial role in overseeing and managing project activities, ensuring smooth progress, and ultimately contributing to project success.
Read also: What are Project Controls
Every project is different, however the theory behind managing them with regards to time, cost and performance, remains the same. PCMs are important across all projects and sectors. The Project Manager directs the work of the project team; however, the PCM drives the delivery of the project, generating the data to assist the PM in making informed project decisions. Think of the PCM as being the navigator and the PM being the pilot. As a PCM, you are responsible for project planning & scheduling, cost estimating & monitoring, progress measurement, risk management, and reporting. You also manage Project Controllers (the risk manager, project scheduler and cost controller) across these areas and report to and provide guidance and consultation to the Project Manager/ PMO lead and Management.
As a direct result of his endeavours and his focus, we have seen a marked improvement in both the quality and consistency of our Project Controls funtion"
Client within the defence sector
From this example the client benefited from clarity in workflows and processes which allow for smoother collaboration and task execution. This newfound clarity has enabled team members to better understand their roles and responsibilities, reducing the likelihood of misunderstandings and delays.
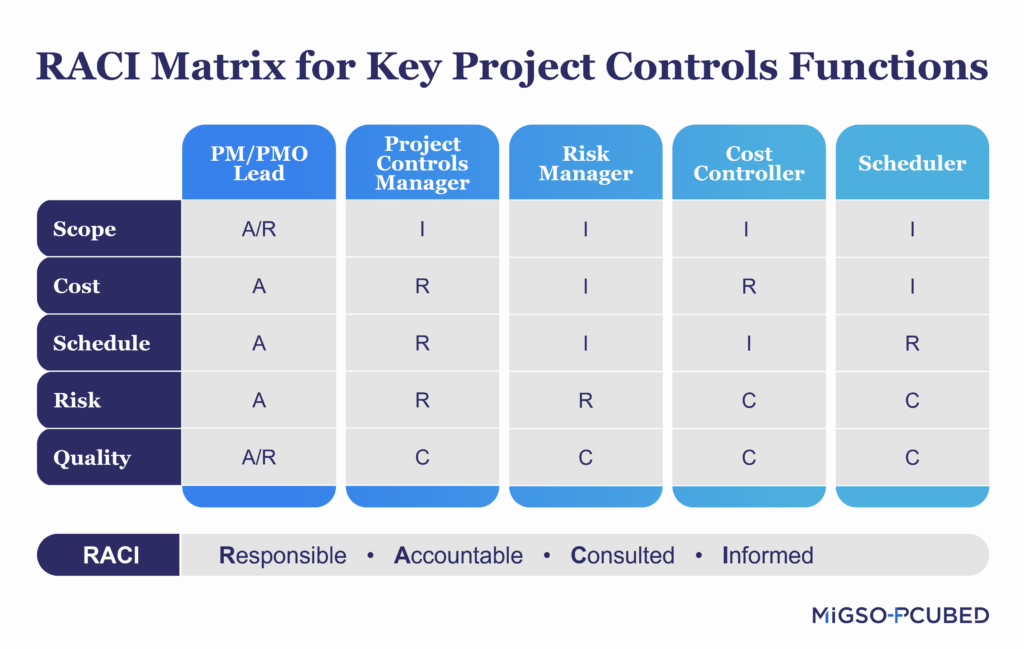
The PCM has a responsibility to each of the project controllers, who are the Risk Manager, Project Scheduler and Cost Manager:
The responsibilities of these people and how they interlink with each other, can be visually displayed in a RACI Matrix.
This RACI Matrix below represents the key outputs of a project, and depicts who is involved and to what extent.
The route to becoming a project controls manager will usually start within the Project Controls function as a project controller, many PCMs will become a subject matter expert within one of the strands of Project Controls and then look to progress to a project control manager role. This means many PCMs will have both the hard skills required as a Project controller as well as the soft skills required for management.
Many of the soft skills are shared across the discipline such as:
In the life of a Project control manager different asks and problems will be faced every day, resulting in transferable skills that can be used across various clients and sectors. At MIGSO-PCUBED, we have established ourselves as experts in Project Controls, providing high quality delivery in a variety of exciting and interesting clients, as well as delivering PC specific training to further support career development
This article was written by Nicky Donowski PMO Manager, Sharnice Atherton-Berry Project Controls Manager and Abdirisaq Essa Project Scheduler
More on the same subject
Loved what you just read?
Let's stay in touch.
No spam, only great things to read in our newsletter.
We combine our expertise with a fine knowledge of the industry to deliver high-value project management services.
MIGSO-PCUBED is part of the ALTEN group.
Find us around the world
Australia – Canada – France – Germany – Italy – Mexico – The Netherlands – Portugal – Romania – South East Asia – Spain – Switzerland – United Kingdom – United States
© 2024 MIGSO-PCUBED. All rights reserved | Legal information | Privacy Policy | Cookie Settings | Intranet
Perfect jobs also result from great environments : the team, its culture and energy.
So tell us more about you : who you are, your project, your ambitions,
and let’s find your next step together.
Dear candidates, please note that you will only be contacted via email from the following domain: migso-pcubed.com. Please remain vigilant and ensure that you interact exclusively with our official websites. The MIGSO-PCUBED Team
Choose your language
Our website is not supported on this browser
The browser you are using (Internet Explorer) cannot display our content.
Please come back on a more recent browser to have the best experience possible
