Our website is not supported on this browser
The browser you are using (Internet Explorer) cannot display our content.
Please come back on a more recent browser to have the best experience possible

Lean Innovation may sound like a hot new buzzword taking over business social media, however it is not new. In the 1990’s businesses spun up Business Process Improvement activities using concepts of Lean to improve productivity, reduce costs, and increase value in the wave of stiff competition, new enterprise technology, and the Internet.
This may sound eerily familiar. With the advent of the fourth industrial revolution, organisations are increasingly attempting to add value while simultaneously cutting costs. Alongside this, they are trying to keep up with the pace of change brought on by digital, artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things.
Enter Lean Innovation, a radical approach to prioritising the right innovations, whether to a product or process, to derive more value for customers with less cost and risk to the organisation. It’s a proven formula for re-engineering the way work is done to better meet the needs of the future.
In addressing the question of what is Lean Innovation? or what is Lean Process Improvement?, it isn’t just ‘Lean Six Sigma’. While Lean Six Sigma is a proven business improvement methodology, Lean Innovation, on the other hand, is a framework. It’s a mindset really, blending the core principles, tools and techniques from Design Thinking, Lean Startup, and Agile, into a catalyst to accelerate an organisation’s portfolio and innovation goals.
At MIGSO-PCUBED, we define Lean Innovation, also referred to as Lean Process Improvement, as an end-to-end solution that delivers rapid innovation by continuously re-engineering processes, products, or services to reduce waste, optimise performance, and maximise value.
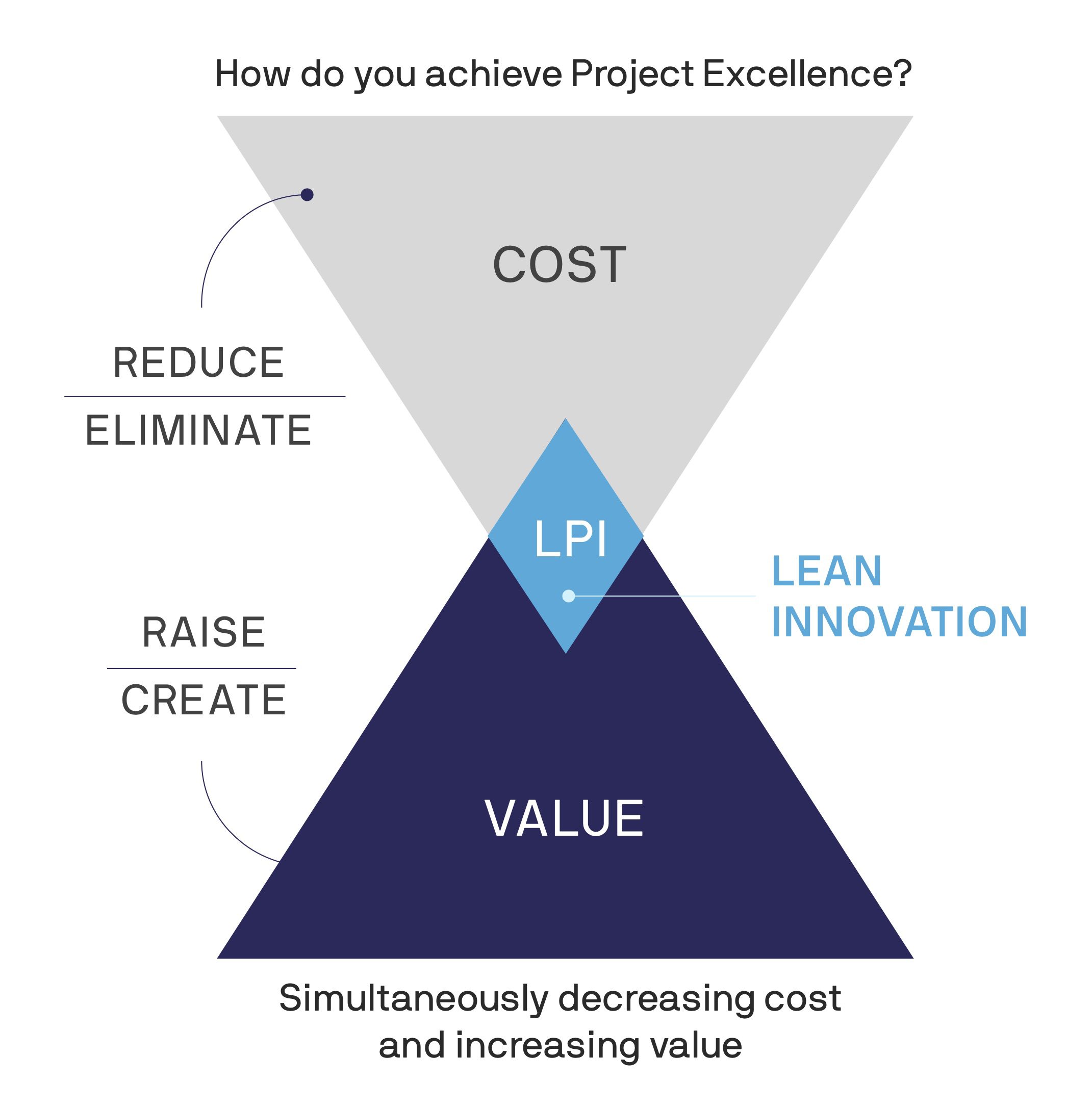
An end-to-end solution that delivers rapid innovation by continuously re-engineering processes, products, or services to reduce waste, optimise performance, and maximise value.
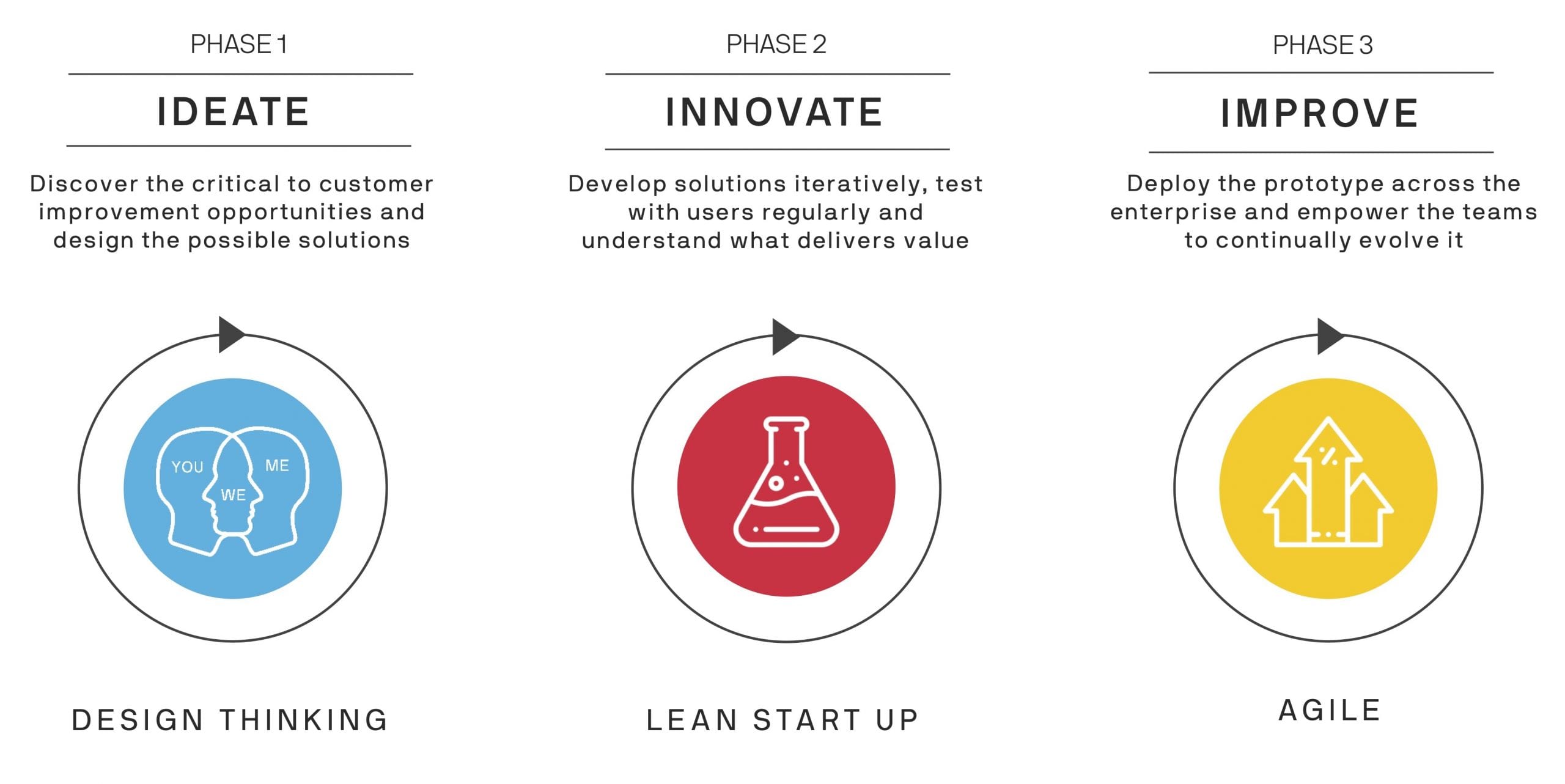
The Lean Innovation Framework, underpinned by Change Management principles, first allows an organisation to identify new improvement opportunities aligned to the needs of the end user using Design Thinking and Lean Six Sigma problem solving.
Second, it provides an approach for rapidly developing and iteratively testing solutions using Lean Startup and Agile ways of working. And finally, for those solutions best aligned to the organisation’s strategy, it utilises Agile for scaling continuous innovation out to the organisation in bite sized increments.
The key benefit is its straightforward methodology centered around learning. Teams begin with identifying a minimum viable product, i.e. the smallest amount of features that will deliver what the end customer really needs and wants. Then the team quickly tests those assumptions in experiments designed to solve a problem with the least amount of investment required. This allows the team to learn early on that the end opportunity will provide value before scaling the additional investment needed to go to market.
Think Big, Start Small, and Adapt Fast.
However, Lean Innovation is not only focused on existing products or business model innovations. In order to get the right products to market faster (i.e. step one in Design Thinking) you also need to focus on people-based innovation and process based innovation. Organisations need to harness their people, their processes, and their purpose to provide a better customer experience.
Lean Innovation draws upon employees’ insights and empowers those closest to the work to deliver the innovations. Champions are nominated to support and drive the improvement process to deliver the organisation’s strategic purpose. These champions are trained in our Lean Innovation methodology allowing the organisation to build an in-house improvement capability.
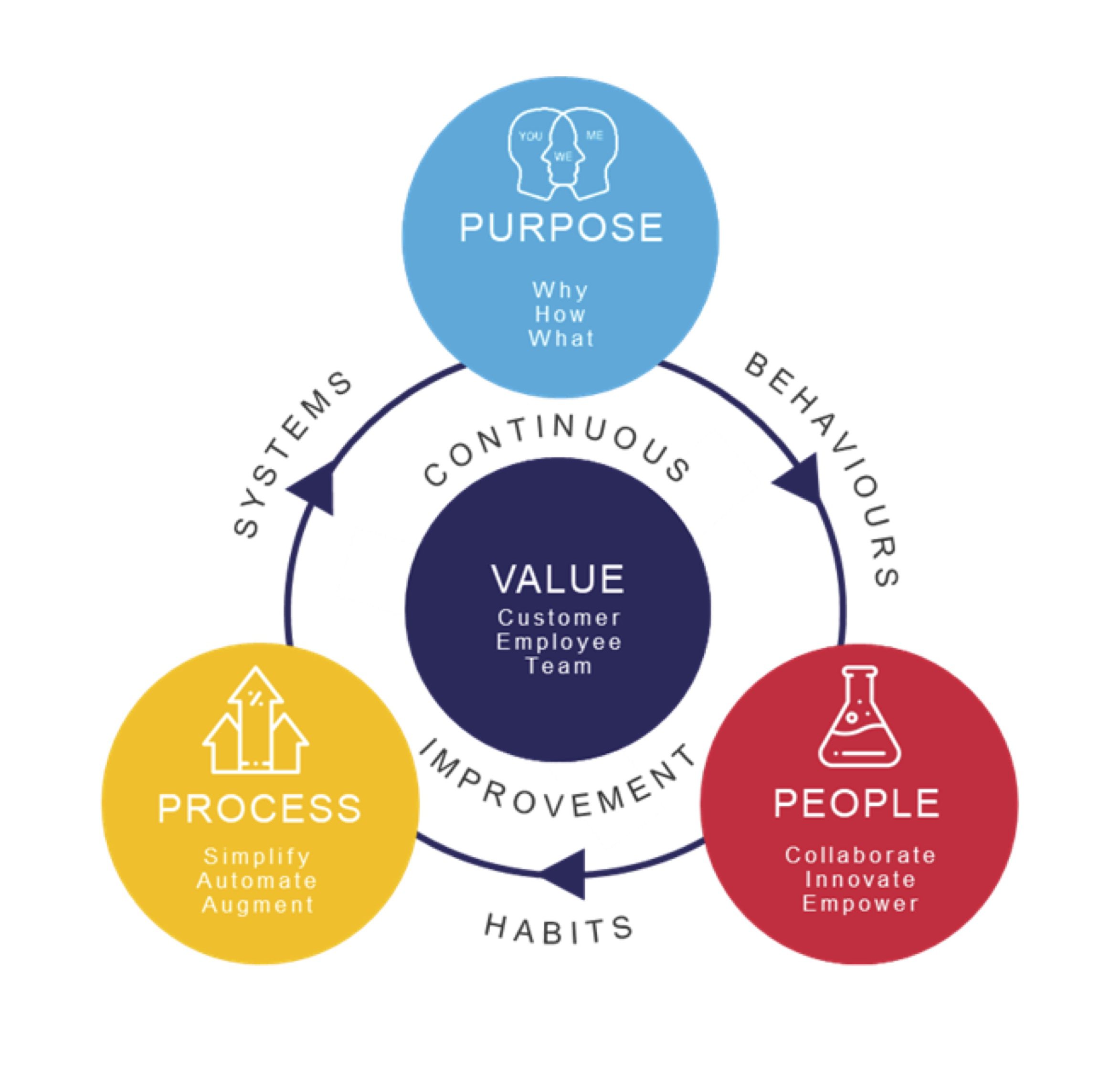
Purpose | People | Process |
|---|---|---|
Alignment on biggest most impactful improvement opportunities | Build in house improvement capability | Increase of value added activities and removal of waste |
Clear line of sight between improvement projects and the value an organisation aims to deliver | Cadre of change champions/ agents | Sustainable transformation, data visualisation and process improvement |
Scalable value driven improvement framework | Commitment for change to a collective vision | Visible portfolio performance data enabling faster decision making |
Alignment & understanding of customer and business requirements | Foundation and roadmap for automated digital solutions |
While there is tremendous value in kicking off a Lean Innovation Transformation, there are also several common blockers organisations face when embarking on this journey. According to the ScienceDirect article on Lean Innovation Management, “Innovation management needs not only a vision and a strategy, but also the appropriate processes to implement innovation, and organisational conditions to facilitate… their implementation.”
We see four main challenges faced in implementing Lean Innovation:
There are many additional challenges faced, as depicted in the graphic below, however the majority of them are interrelated. Fixing one, often has a knock on effect to improving another.
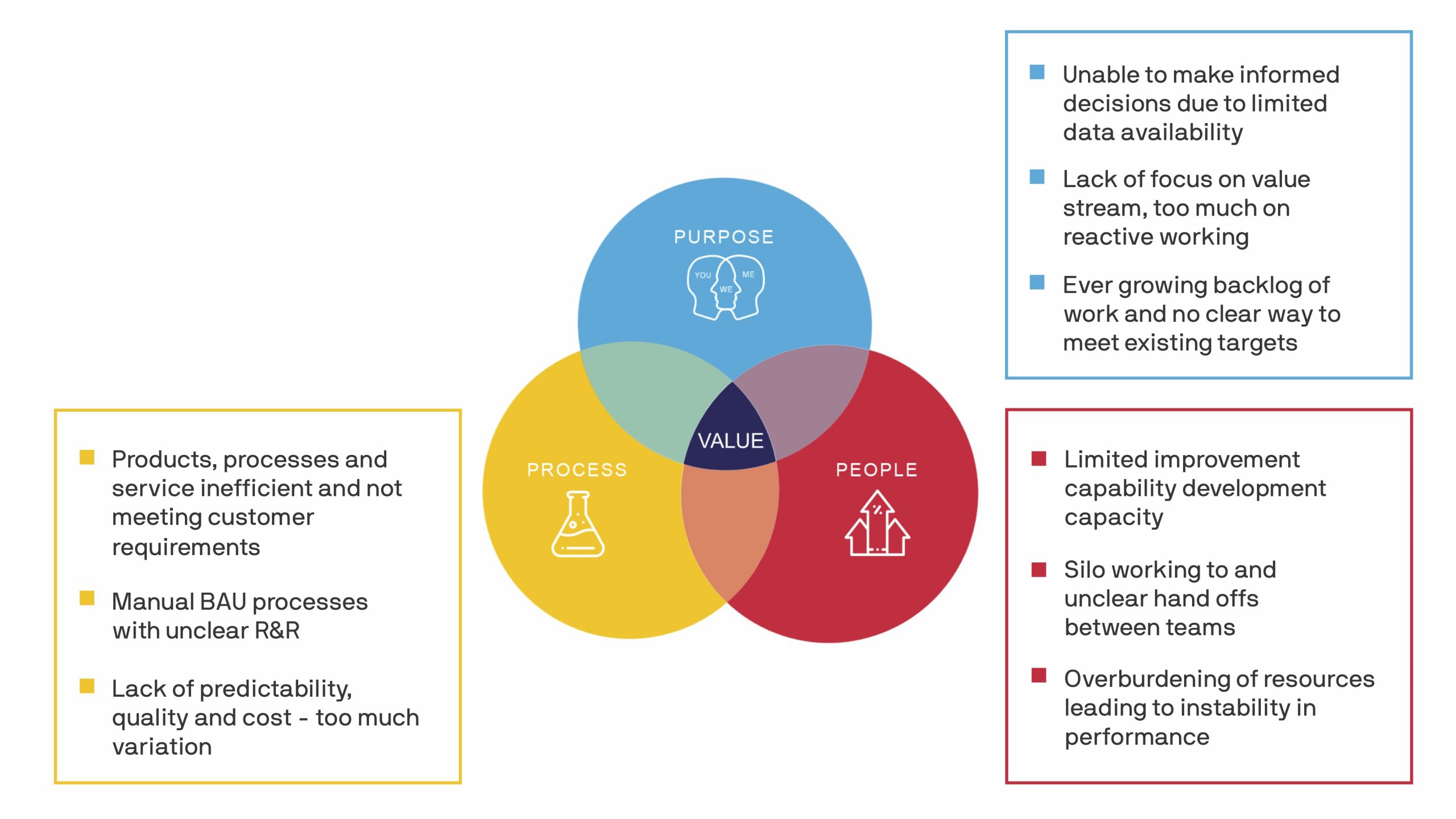
In the first challenge, knowing the right opportunities to invest in, the unfortunate situation is that there is no shortage of ideas on where to improve. With an ever-growing backlog of work, resources are overburdened often leading to poor performance. Recently P&G published a case study on their own Lean Innovation Transformation. In the case study, they say one of the keys to their success was the ability to use data to tell them which areas to fund.
With the advent of Industry 4.0, organisations find themselves with increasing amounts of data. However, extracting value from such vast data lakes requires the development of new internal capabilities and the adoption of new technical solutions.
With Lean Innovation, we typically develop a visual management board to show in real-time the programme, the process, and the progress of the improvement. The live and accurate data enables informed management decisions and can visually highlight team performance.
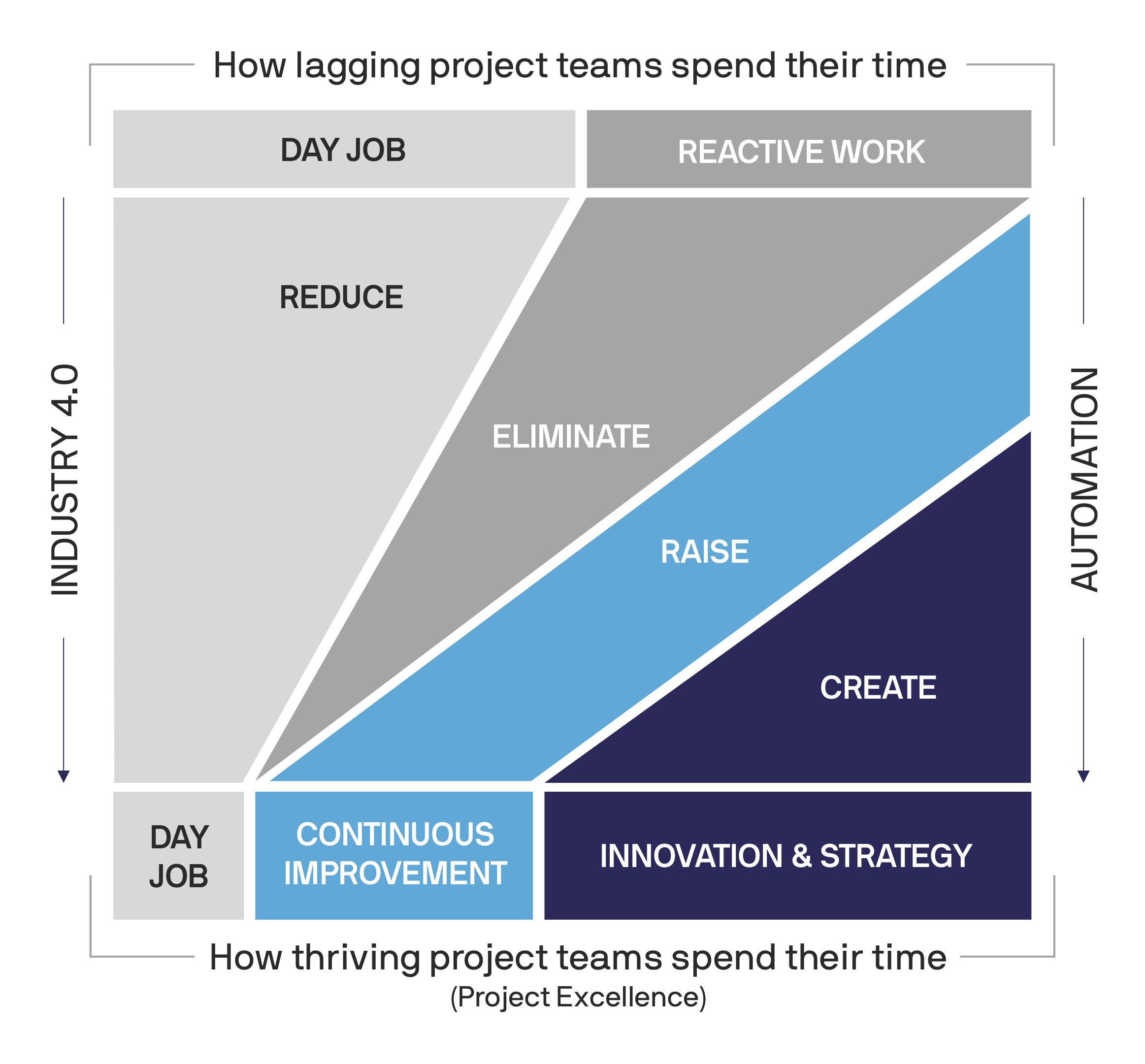
The second challenge of implementing Lean Innovation is that many project teams are spending a majority of their day performing manual tasks and reactive work. Nearly 40% of workers say they spend a third of their week on repetitive tasks. As such, teams have a reduced opportunity to concentrate on activities that contribute or align to furthering the company’s strategic vision.
Lean Innovation looks to promote a focus on value and the elimination of waste. Teams investigate ways to streamline processes to reduce their hours spent on their day job, employing automation, and embedding technical solutions. Streamlining processes allows teams to thrive, allowing them to spend more time on continuous improvement, and provides more capacity for teams to concentrate on innovation and strategy.
The third challenge is how to manage the execution and delivery of benefits from innovation. MIGSO-PCUBED partners with clients to deliver lean process improvement consulting services. We blend the best of Lean Six Sigma, Design Thinking, Lean Start, and SAFe Agile with our core expertise in both Program & Project Management and Organisational Change Management to drive innovation delivery.
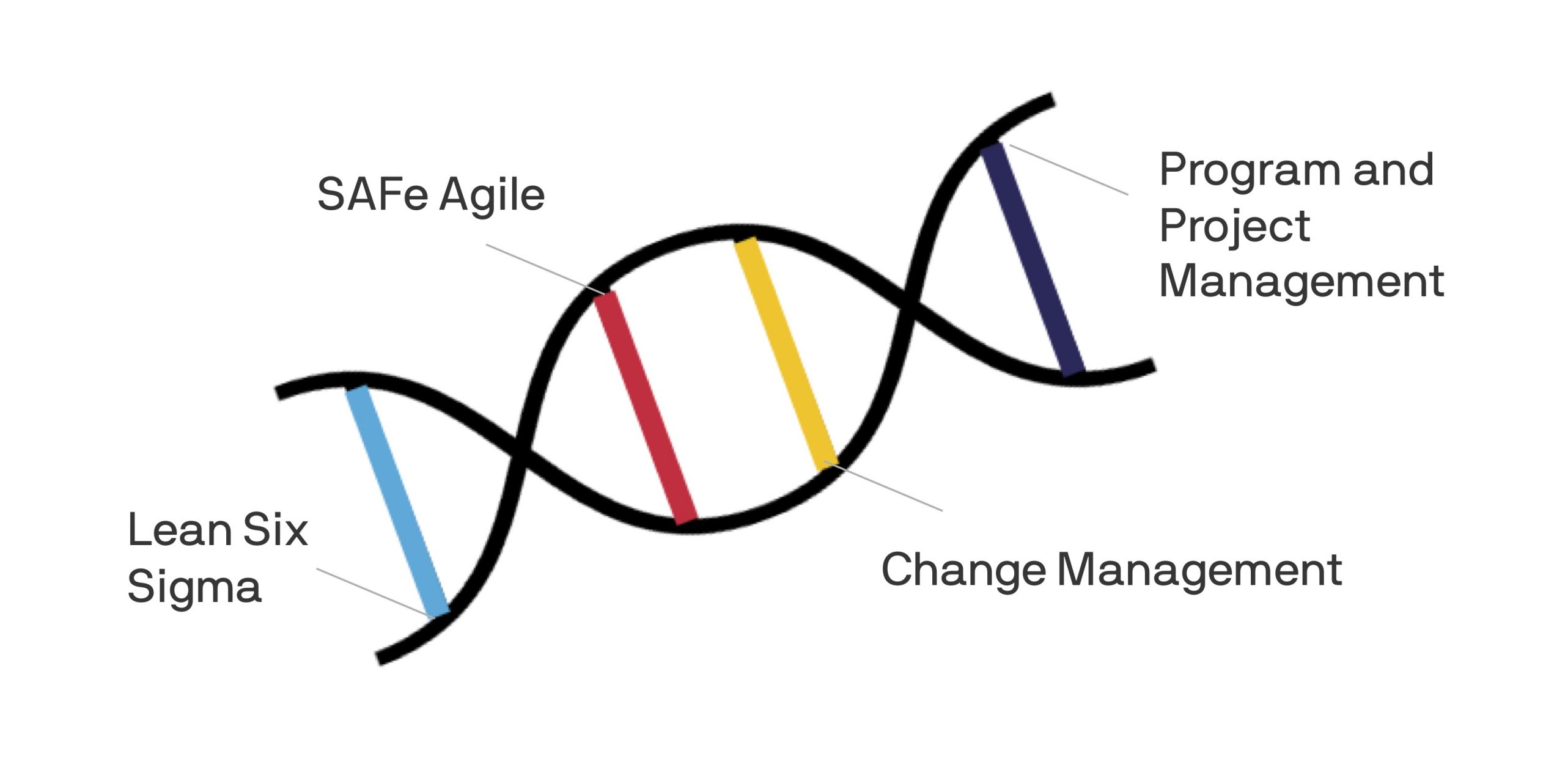
The MIGSO-PCUBED Lean Innovation Framework is built on the core Lean Innovation principle of think big, start small, and adapt fast. It has three distinct phases of Ideate, Innovate, and Improve explained in further detail below.
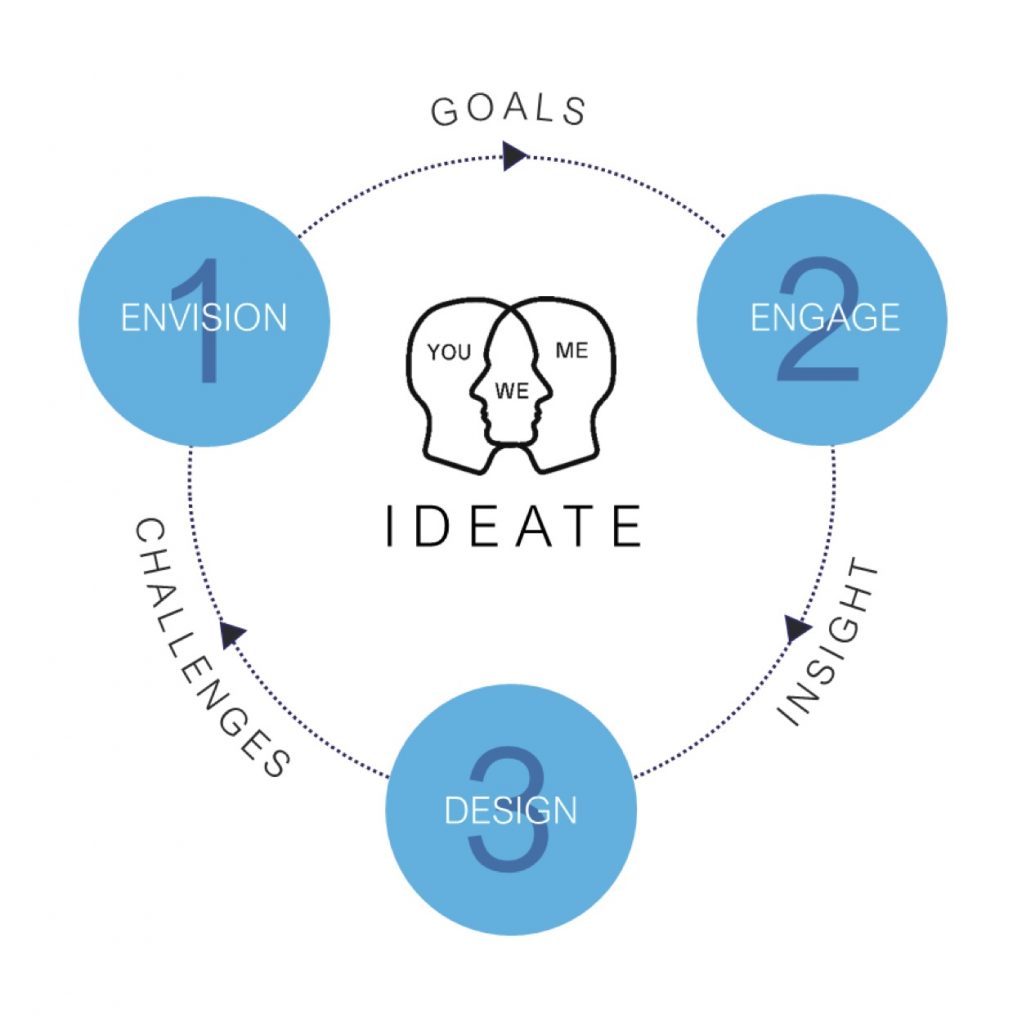
Phase 1: Ideate – Think Big
Envision: Discover the needs of your customers and develop a vision with value at the heart of it
Engage: With a goal in mind, understand where the pain is today within the process and measure the performance
Design: With new insight, identify the root causes to the problem, generate solutions collectively, and gain sponsorship to fulfill the challenge
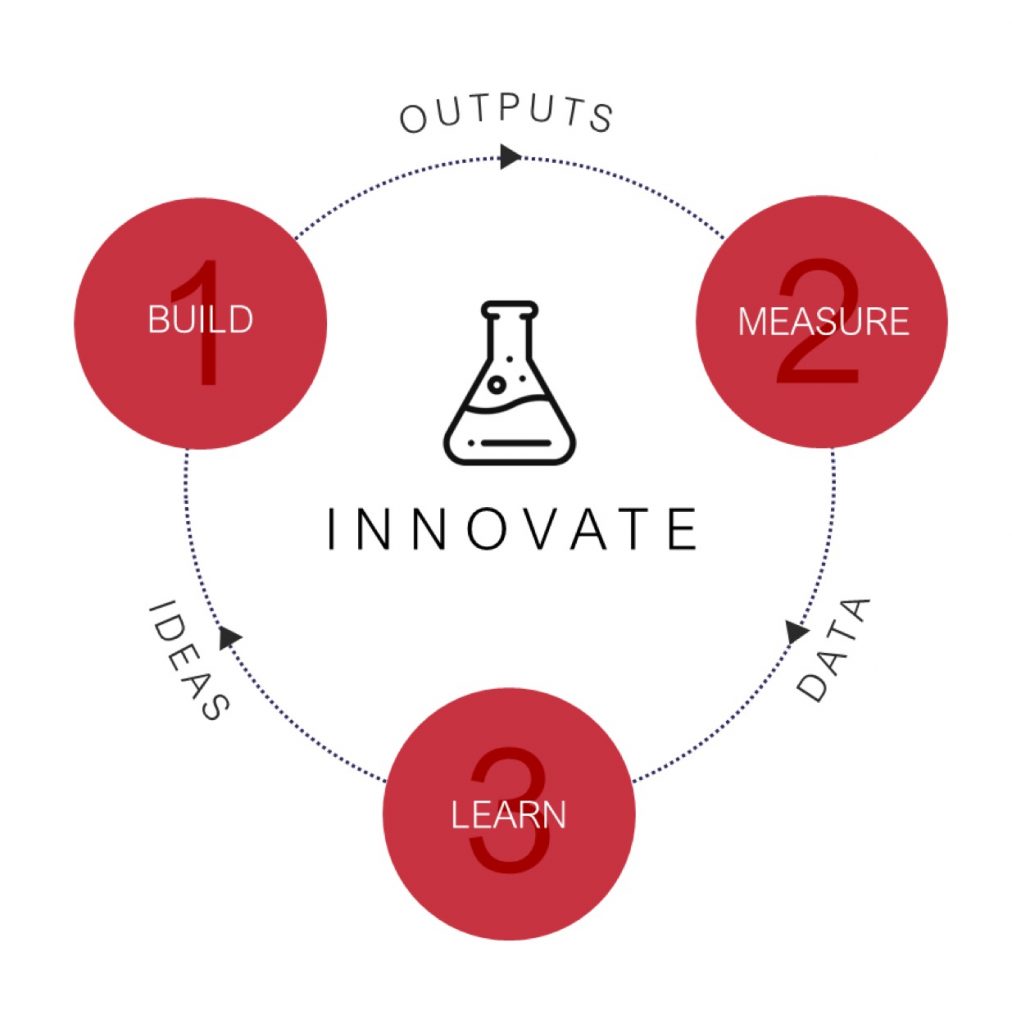
Phase 2: Innovate – Start Small
Build: Build a minimum viable product (MVP) focused on delivering value as soon as possible
Measure: Test and measure performance of your outputs. See how your customers respond, learn, and adapt accordingly
Learn: Using data and evidence, understand what activities deliver value and which are waste. Form new ideas, Pivot or Persevere
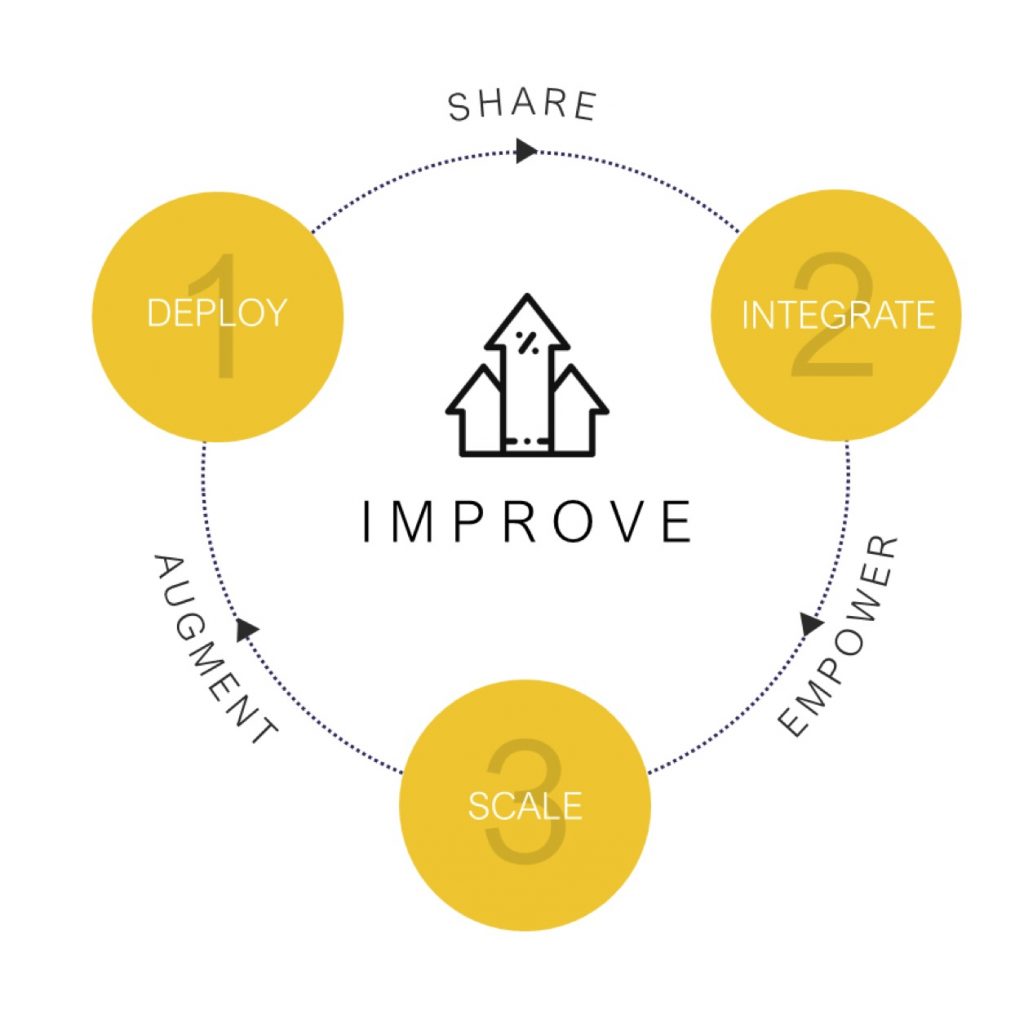
Phase 3: Improve – Adapt Fast
Deploy: With a proven prototype embedded, prepare your enterprise to trailblaze the transformation
Integrate: Share the learning by bringing teams together to pioneer the new way of working within their own areas
Scale: Empower the organisation to maximise the benefits of the transformation by embedding the change as business as usual and continuously augment
The final roadblock often faced in innovation transformation is that organisations just starting on their journey haven’t built either the capability or time for innovation. In order to get over this initial resistance we utilise short time-blocked sprints combined with facilitated workshops. Two critical pieces are the Voice of the Customer Workshops and Rapid Ideation Events.
Voice of the Customer workshops are done at the start of a Lean Innovation journey. They are run with people who actually perform the work to identify your organisation’s largest improvement opportunities.
Rapid Ideation Events are workshops run during Phase 1, the Ideate phase. They aim to understand which activities deliver value and which deliver waste within improvement workstreams. Solutions are developed within the 3 day workshop and receive on the spot approval from senior sponsors. Teams then will build and test in the subsequent phase for approved ideas. Focusing on defining and analysing activities ensures value is truly added.We have used our Lean Innovation methodology with various clients in Nuclear, Automotive, Pharmaceuticals to help them overcome their initial hurdles, resistance to change, and allow them to see change sooner.
This article was written by Dan Hamilton and James Humberstone
Think big. Start small. Adapt fast. Re-engineering processes, products, and services to eliminate waste, optimise performance, and maximise value.
We combine our expertise with a fine knowledge of the industry to deliver high-value project management services.
MIGSO-PCUBED is part of the ALTEN group.
Find us around the world
Australia – Canada – France – Germany – Italy – Mexico – The Netherlands – Portugal – Romania – South East Asia – Spain – Switzerland – United Kingdom – United States
© 2024 MIGSO-PCUBED. All rights reserved | Legal information | Privacy Policy | Cookie Settings | Intranet
Perfect jobs also result from great environments : the team, its culture and energy.
So tell us more about you : who you are, your project, your ambitions,
and let’s find your next step together.
Dear candidates, please note that you will only be contacted via email from the following domain: migso-pcubed.com. Please remain vigilant and ensure that you interact exclusively with our official websites. The MIGSO-PCUBED Team
Choose your language
Our website is not supported on this browser
The browser you are using (Internet Explorer) cannot display our content.
Please come back on a more recent browser to have the best experience possible
